| Colour |
Wavelength |
| red |
700 - 640 nm |
| orange |
640 - 600 nm |
| yellow |
600 - 555 nm |
| green |
555 - 485 nm |
| blue |
485 - 430 nm |
| violet |
430 - 380 nm |
COLOURS-OF-THE-RAINBOW
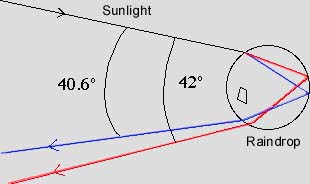
The best known natural example of colour
separation through refraction is the rainbow. In
sunlight all colours of the spectrum are present and
due to a refraction in water particles in the
atmosphere, a rainbow emerges with seven
distinguished bands in the colours red, orange,
yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet with a more or
less gradually transition from one colour to
another. Individual drops of water in a rain shower,
in a fountain or in a curtain of water from a garden
hose act as small prisms that partially let pass the
light and partially refract it. The angle of refraction
depends on the wavelengths of the different colour
components of the incoming light, an effect that we
observe as a rainbow. There is no widely accepted
standardisation of the wavelengths of the different
colours. The table listed below is therefore an
indication only.